主要代码:
CReqRepMachine::CReqRepMachine(const PortGroup& pg, int hwm) : m_port_group(pg)
{
zmq::context_t& context = DCContext::Instance().ZmqContext();
// std::cout << "hwm: " << hwm << std::endl;
// 请求链路
m_socket_front.reset(new zmq::socket_t(context, zmq::socket_type::router));
m_socket_front->setsockopt(ZMQ_RCVHWM, hwm);
m_socket_front->setsockopt(ZMQ_SNDHWM, hwm);
m_socket_back.reset(new zmq::socket_t(context, zmq::socket_type::dealer));
m_socket_back->setsockopt(ZMQ_RCVHWM, hwm);
m_socket_back->setsockopt(ZMQ_SNDHWM, hwm);
// 回报链路
// m_socket_front_1.reset(new zmq::socket_t(context, zmq::socket_type::push));
// m_socket_back_1.reset(new zmq::socket_t(context, zmq::socket_type::pull));
}
void PersistQrySpi::Init()
{
if (m_action_api == nullptr)
{
m_action_api = IActionServerApi::CreateApi(this);
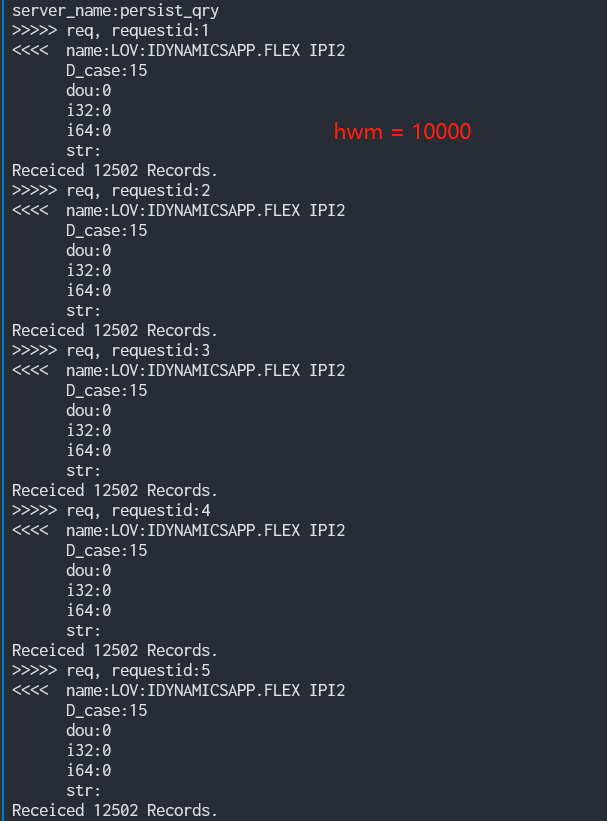
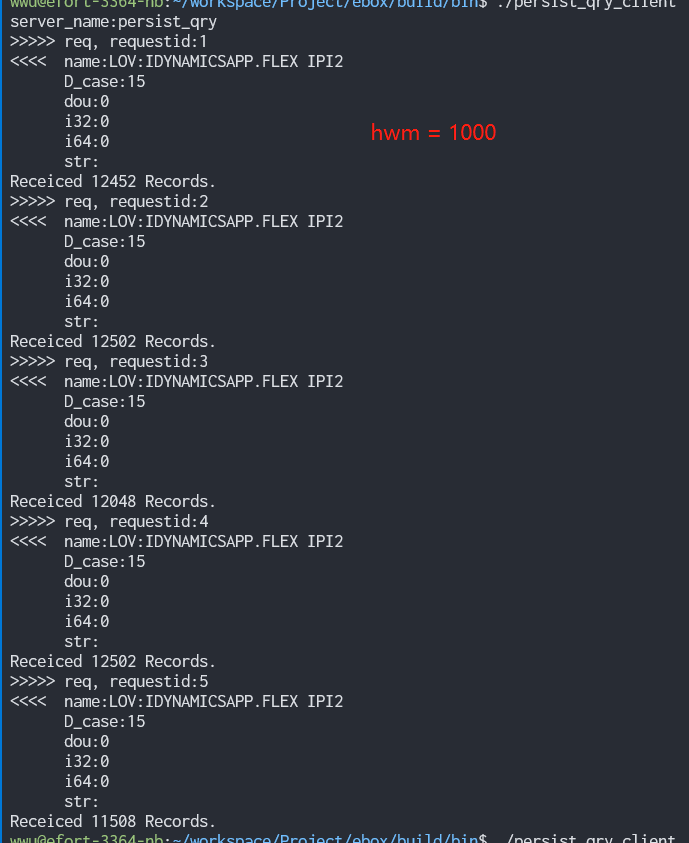
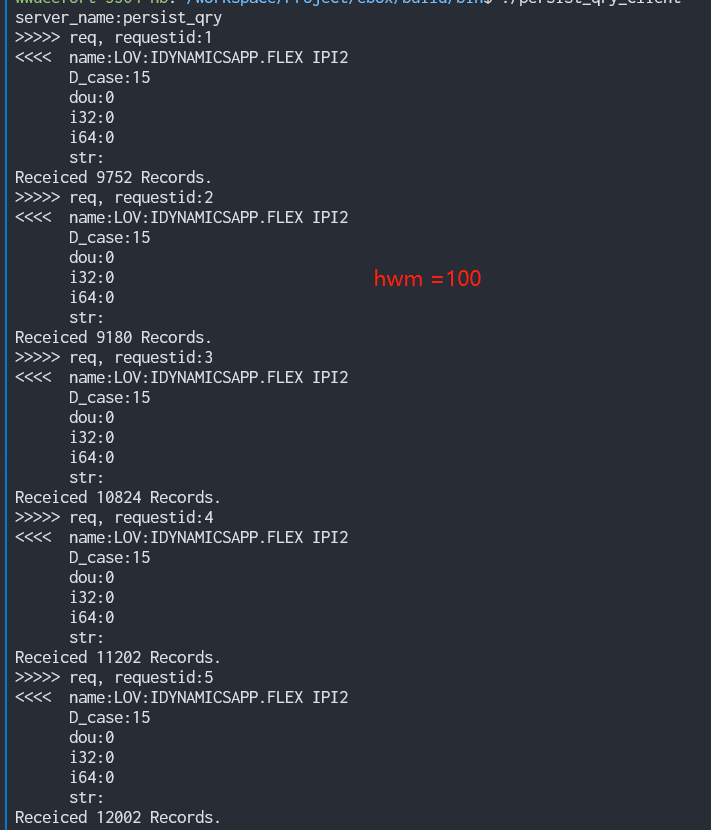
m_action_api->SetHighWaterMark(1000);
m_action_api->Connect("persist_qry");
}
}数据库内数据条数:
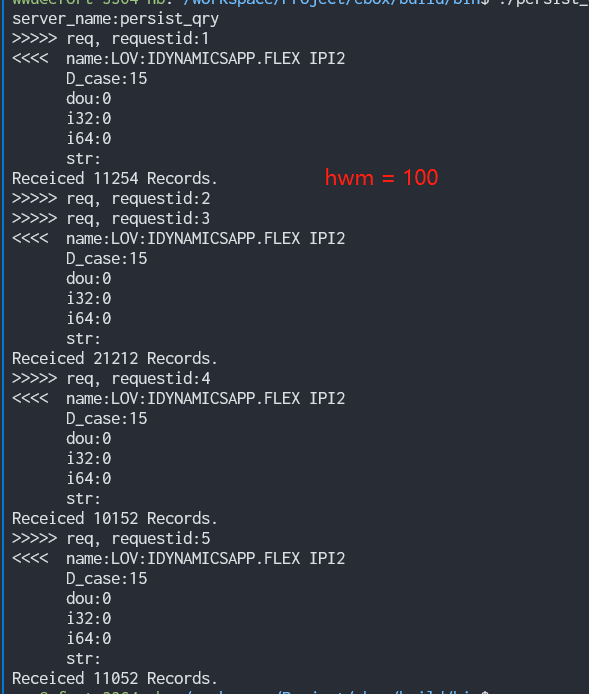
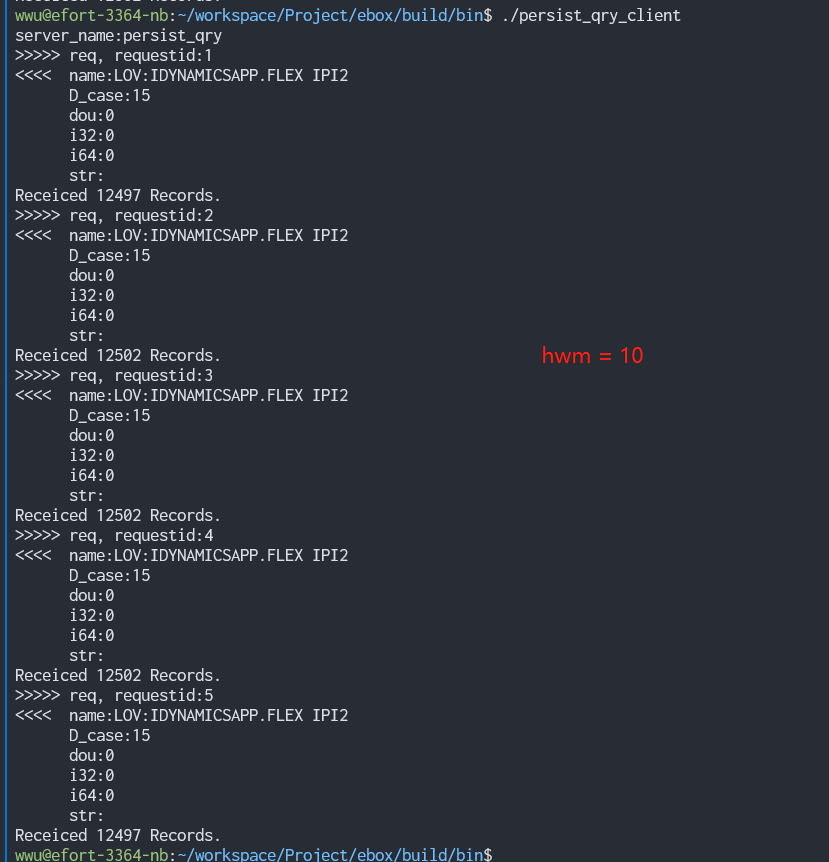
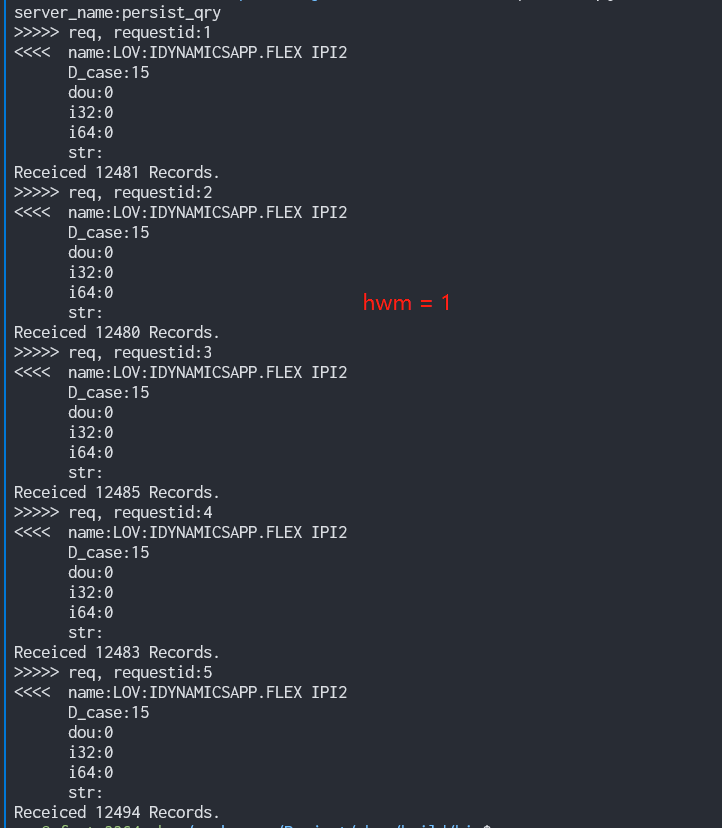
调研
2. Sockets and Patterns | ØMQ - The Guide (zeromq.org)
ZeroMQ uses the concept of HWM (high-water mark) to define the capacity of its internal pipes. Each connection out of a socket or into a socket has its own pipe, and HWM for sending, and/or receiving, depending on the socket type. Some sockets (PUB, PUSH) only have send buffers. Some (SUB, PULL, REQ, REP) only have receive buffers. Some (DEALER, ROUTER, PAIR) have both send and receive buffers.
ZeroMQ 使用 HWM(高水位线)的概念来定义其内部管道的容量。每个从套接字发出或进入套接字的连接都有自己的管道,以及用于发送和/或接收的 HWM,具体取决于套接字类型。某些套接字(PUB、PUSH)仅具有发送缓冲区。有些(SUB、PULL、REQ、REP)仅具有接收缓冲区。有些(DEALER、ROUTER、PAIR)同时具有发送和接收缓冲区。
In ZeroMQ v2.x, the HWM was infinite by default. This was easy but also typically fatal for high-volume publishers. In ZeroMQ v3.x, it’s set to 1,000 by default, which is more sensible. If you’re still using ZeroMQ v2.x, you should always set a HWM on your sockets, be it 1,000 to match ZeroMQ v3.x or another figure that takes into account your message sizes and expected subscriber performance.
在 ZeroMQ v2.x 中,HWM 默认是无限的。这很容易,但对于大批量出版商来说通常也是致命的。在 ZeroMQ v3.x 中,默认设置为1,000,这是更合理的。如果您仍在使用 ZeroMQ v2.x,则应始终在套接字上设置 HWM,可以是 1,000 以匹配 ZeroMQ v3.x,也可以是考虑到消息大小和预期订阅者性能的其他数字。
When your socket reaches its HWM, it will either block or drop data depending on the socket type. PUB and ROUTER sockets will drop data if they reach their HWM, while other socket types will block. Over the inproc transport, the sender and receiver share the same buffers, so the real HWM is the sum of the HWM set by both sides.
当您的套接字达到其 HWM 时,它将根据套接字类型阻止或删除数据。 PUB 和 ROUTER 套接字如果达到其 HWM 将丢弃数据,而其他套接字类型将阻塞。在 inproc 传输中,发送方和接收方共享相同的缓冲区,因此真正的 HWM 是双方设置的 HWM 之和。
Lastly, the HWMs are not exact; while you may get up to 1,000 messages by default, the real buffer size may be much lower (as little as half), due to the way libzmq implements its queues.
最后,HWM 并不精确;虽然默认情况下您最多可以获得 1,000 条消息,但由于 libzmq 实现其队列的方式,实际缓冲区大小可能要低得多(只有一半)。
原文 How does the HWM (high water mark) work with any socket type?
On PUB and ROUTER sockets, when the SNDHWM is reached on outgoing pipes, messages are dropped. DEALER and PUSH sockets will block when their outgoing pipes are full. On incoming pipes, SUB sockets will drop received messages when they reach their RCVHWM. PULL and DEALER sockets will refuse new messages and force messages to wait upstream due to TCP backpressure.
翻译 HWM(高水位标记)与各种套接字类型一起使用时会发生什么事?
在 PUB 和 ROUTER 类型套接字上,当在传出管道上达到 SNDHWM 时,将会丢弃消息。而 DEALER 和 PUSH 类型套接字将会堵塞。在传入管道上,到达 RCVHWM 时,SUB 类型套接字将会丢弃消息,而 PULL 和 DEALER 套接字将拒绝新消息并强制消息在上游等待。